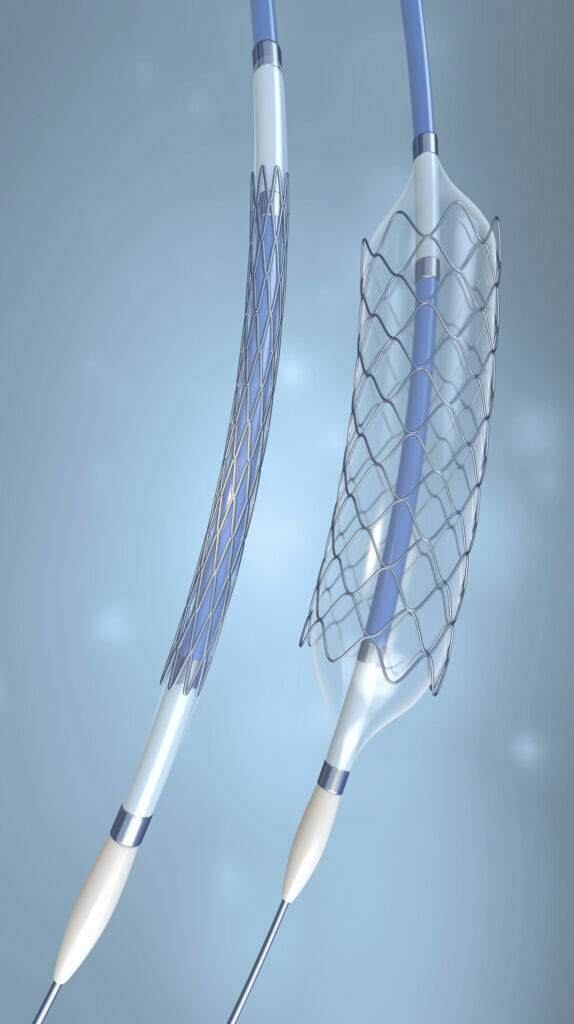
Polymeric balloons are commonly located at the distal end of certain catheters for a variety of medical applications. These include position retention in urological catheters, and dilation of gastrointestinal strictures and coronary angioplasty.
Catheter balloons have extremely thin and flexible walls to allow them to be deflated and compressed into a small space for transit to the designated site. They are also designed for high strength when expanded under pressure to enlarge narrow openings and deploy stents.
Catheter balloons are manufactured by blow molding extruded tubes made from specific polymers. These polymers must have sufficient flexibility for deflation and inflation, and good mechanical strength to high resist burst pressures when expanded. High durometer polyether block amide such as Pebax® 7233 SA 01 MED, Rilsan® BMNO MED, and Rilsamid® AMNO are considered for catheter balloon applications.